
- Media library
- Question limits
- Creating a survey from MS Word doc
- How to edit live surveys
- Survey blocks
- Survey block randomizer
- Question randomization
- Scale Library
- What is monadic testing?
- What is sequential monadic testing?
- Extraction Support for Image Chooser Question Types
- What is comparison testing?
- Custom validation messages
- Survey Builder with QxBot
- Standard question types
- Advanced question types
- Multiple choice question type
- Text question- comment box
- Matrix multi-point scales question type
- Rank order question
- Smiley-rating question
- Image question type
- Date and time question type
- CAPTCHA question type
- Net Promoter Score question type
- Van Westendorp's price sensitivity question
- Choice modelling questions
- Side-By-Side matrix question
- Homunculus question type
- Predictive answer options
- Presentation text questions
- Multiple choice: select one
- Multiple choice: select many
- Page timer
- Contact information question
- Matrix multi-select question
- Matrix spreadsheet question
- Closed card sorting question
- Flex Matrix
- Text Slider Question Type
- Graphical Rating Scales
- Rank Order - Drag and Drop
- Bipolar Matrix - Slider
- Bipolar Matrix Likert Scale
- Gabor Granger
- Verified Digital Signature
- Star Rating Question Type
- Push to social
- Attach Upload File Question
- Constant Sum Question
- Video Insights
- Answer type
- Reorder questions
- Question tips
- Text box next to question
- Text question settings
- Adding other option
- Matrix question settings
- Image rating question settings
- Scale options for numeric slider question
- Constant sum question settings
- Budget scale question settings
- Setting default answer option
- Exclusive option for multiple choice questions
- Validate question
- Bulk validation settings
- Remove validation message
- Question separators
- Question Code
- Page breaks in survey
- Survey introduction with acceptance checkbox
- RegEx Validation
- Question Library
- Embed Media
- Slider Start Position
- Answer Display - Alternate Flip
- Matrix - Auto Focus Mode
- Text validations
- Numeric Input Settings- Spreadsheet
- Answer Groups
- Hidden Questions
- Decimal Separator Currency Format
- Allow Multiple Files - Attache/Upload Question Type
- Text box - Keyboard input type
- Add logo to survey
- Custom Themes
- Display Settings
- Auto-advance
- Progress bar
- Automatic question numbering option
- Enabling social network toolbar
- Browser Title
- Print or export to PDF, DOC
- Survey Navigation Buttons
- Accessible Theme
- Back and Exit Navigation Buttons
- Focus Mode
- Default Display Mode
- Visual Display Mode
- Branching - Skip Logic
- Compound Branching
- Compound or delayed branching
- Response Based Quota Control
- Dynamic text or comment boxes
- Extraction logic
- Show or hide question logic
- Dynamic show or hide
- Scoring logic
- Net promoter scoring model
- Piping text
- Survey chaining
- Looping logic
- Branching to terminate survey
- Logic operators
- Selected N of M logic
- JavaScript Logic Syntax Reference
- Block Flow
- Block Looping
- Scoring Engine: Syntax Reference
- Always Extract and Never Extract Logic
- Matrix Extraction
- Locked Extraction
- Dynamic Custom Variable Update
- Survey settings
- Save & continue
- Anti Ballot Box Stuffing (ABBS) - disable multiple responses
- Deactivate survey
- Admin confirmation email
- Action alerts
- Survey timeout
- Finish options
- Spotlight report
- Print survey response
- Search and replace
- Review Mode
- Survey Timer
- Allowing multiple respondents from the same device
- Text Input Size Settings
- Admin Confirmation Emails
- Survey Close Date
- Respondent Location Data
- Review Mode
- Review, Edit and Print Responses
- Geo coding
- Dynamic Progress Bar
- Response Quota
- Live survey URL
- Customize survey URL
- Create email invitation
- Personalizing emails
- Email invitation settings
- Email list filter
- Survey reminders
- Export batch
- Email status
- Spam index
- Send surveys via SMS
- Phone & paper
- Adding responses manually
- SMS Pricing
- Embedding Question In Email
- Deleting Email Lists
- Multilingual Survey Distribution
- SMTP
- Reply-To Email Address
- Domain Authentication
- Email Delivery Troubleshooting
- Survey Dashboard - Report
- Overall participant statistics
- Dropout analysis
- Pivot table
- Turf analysis
- Trend analysis
- Correlation analysis
- Survey comparison
- Gap analysis
- Mean calculation
- Weighted mean
- Spider chart
- Cluster Analysis
- Dashboard filter
- Datapad
- Download Options - Dashboard
- HotSpot analysis
- Heatmap analysis
- Weighted Rank Order
- Cross-Tabulation Grouping Answer Options
- A/B Testing in QuestionPro Surveys
- Data Quality
- Data Quality Terminates
- Matrix Heatmap Chart
- Column proportions test
- Conjoint analysis designs
- Conjoint part worths calculation
- Conjoint calculations and methodology
- Conjoint attribute importance
- Conjoint profiles
- Market segmentation simulator
- Conjoint brand premium and price elasticity
- What is MaxDiff scaling
- MaxDiff settings
- Anchored MaxDiff Analysis [BETA Release]
- MaxDiff FAQ
- MaxDiff- Interpreting Results
- Automatic email report
- Data quality - Patterned responses
- Data quality - gibberish words
- Import external data
- Download center
- Consolidate report
- Delete survey data
- Data quality - All checkboxes selected
- Exporting data to Word or Powerpoint
- Scheduled reports
- Datapad
- Notification Group
- Unselected Checkbox Representation
- Merge Data 2.0
- Plagiarism Detection
- IP based location data
- Update user details
- Update time zone
- Teams
- Add Users
- Usage dashboard
- Single user license
- License restrictions
- Troubleshooting login issues
- Software support package
- Welcome Email
- User Roles & Permissions
- Bulk Add Users
- Two-Factor Authentication
- Network Access
- Changing ownership of the survey
- Unable to access Chat support
- Navigating QuestionPro Products
Conjoint Analysis – Profiles
A conjoint profile is a set of attributes with different levels that are displayed for selection. Respondents would be shown a set of products, prototypes, mockups, or pictures created from a combination of levels from all or some of the constituent attributes and asked to choose from the products they are shown. Each example is similar enough that consumers will see them as close substitutes, but dissimilar enough that respondents can clearly determine a preference. Each example is composed of a unique combination of product features.
To view detailed Profiles:
Go to: Login » Surveys » Reports » Choice Modelling » Conjoint Analysis » Profiles
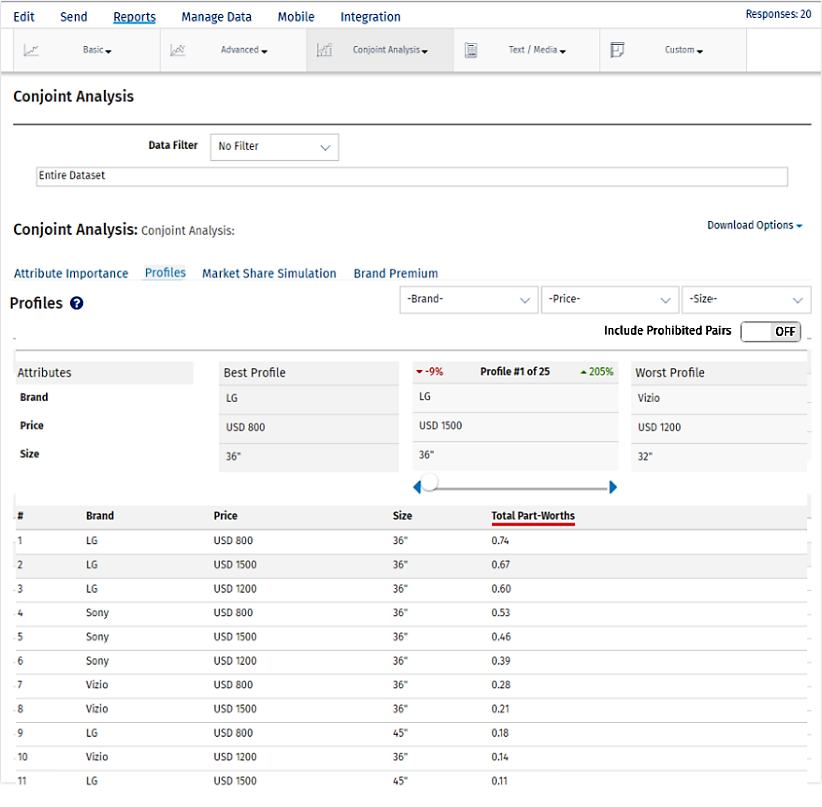
By default results displayed will be excluding prohibited pairs if any selected by the users in the beginning .
The best profile is always displayed on the left and the worst profile on the right. In between, you can select a custom profile to see how it compares with the best and the worst profile.If any pair is selected in prohibited pair that will not be displayed in best, worst or custom profile.If user still want to see the prohibited pairs they can enable the including prohibited pairs option provided.
For the selected profile, you can see the percentage point difference between the best profile and the selected profile in red.
The percentage point difference between the worst profile and the selected profile is displayed in green.
You can also limit/narrow down on the profiles by selecting specific levels for the attributes.
Attribute and level with highest Total Part Worth Value will be selected as the Best Profile and the one with lowest Total Part Worth value will be selected as the Worst Profile.
Calculating Part-Worths Values
We use the following algorithm to calculate CBC Conjoint Part-Worths:
Notation
Let there be R respondents, with individuals r = 1 ... RLet each respondent see T tasks, with t = 1 ... T
Let each task t have C configurations (or concepts), with c = 1 ... C (C in our case is usually 3 or 4)
If we have A attributes, a = 1 to A, with each attribute having La levels, l = 1 to La, then the part-worth for a particular attribute/level is w’(a,l). It is this (jagged array) of part worths we are solving for in this exercise.
We can simplify this to a one-dimensional array w(s), where the elements are:{w’(1,1), w’(1,2) ... w’(1,L1), w’(2,1) ... w’(A,LA)} with w having S elements.
A specific configuration x can be represented as a one-dimensional array x(s), where x(s)=1 if the specific level/attribute is present, and 0 otherwise.
Let Xrtc represent the specific configuration of the cth configuration in the tth task for the rth respondent. Thus the experiment design is represented by the four dimensional matrix X with size RxTxCxS
If respondent r chooses configuration c in task t then let Yrtc=1; otherwise 0.
Utility Of A Specific Configuration
The Utility Ux of a specific configuration is the sum of the part-worths for those attribute/levels present in the configuration, i.e. it is the scalar product x.wThe Multinomial Logit Model
For a simple choice between two configurations, with utilities U1 and U2, the MNL model predicts that configuration 1 will be chosenEXP(U1)/(EXP(U1) + EXP(U2)) of the time (a number between 0 and 1).
For a choice between N configurations, configuration 1 will be chosen
EXP(U1)/(EXP(U1) + EXP(U2) + ... + EXP(UN)) of the time.
Modeled Choice Probability
Let the choice probability (using MNL model) of choosing the cth configuration in the tth task for the rth respondent be:Prtc=EXP(xrtc.w)/SUM(EXP(xrt1.w), EXP(xrt2.w), ... , EXP(xrtC.w))
Log-likelihood Measure
The Log-Likelihood measure LL is calculated as:
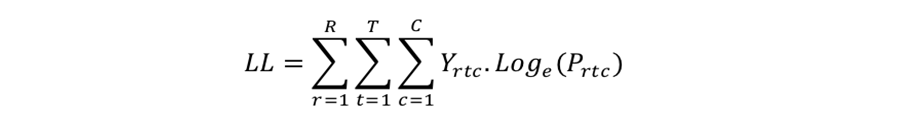
Prtc is a function of the part-worth vector w, which is the set of part-worths we are solving for.
Solving For Part-worths Using Maximum Likelihood
We solve for the part-worth vector by finding the vector w that gives the maximum value for LL. Note that we are solving for S variables.This is a multi-dimensional non-linear continuous maximization problem, and requires a standard solver library. We use the Nelder-Mead Simplex Algorithm.
The Log-Likelihood function should be implemented as a function LL(w, Y, X), and then optimized to find the vector w that gives us a maximum. The responses Y, and the design X are given, and constant for a specific optimization. Initial values for w can be set to the origin 0.
The final part-worths w are re-scaled so that the part-worths for any attribute have a mean of zero, simply by subtracting the mean of the part-worths for all levels of each attribute.

